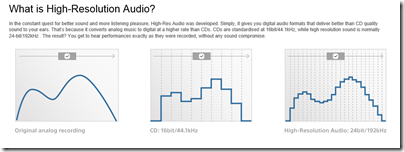
Sony’s top of the range wireless speaker grabbed my attention because it is not just a Bluetooth and Apple AirPlay speaker, but also the entry-level device in Sony’s push for high resolution audio, billed as better than CD quality. Get all the ducks in line, and you can play DSD (the format of SACD) downloads directly through this device, or high-resolution PCM at up to 32-bit/192kHz. It has the speaker technology to go with it too: sub-woofer for deep bass (within the limitations of a small box), and super tweeters for extended high frequencies up to a rumoured 40kHz, though I cannot find detailed specification from Sony. Note that this is well beyond what humans can hear.
In the box you get the wireless speaker, remote, polishing cloth, mains cable, two odd little sticks which, it turns out, are tools for removing the front grille, and a couple of short leaflets in multiple languages.
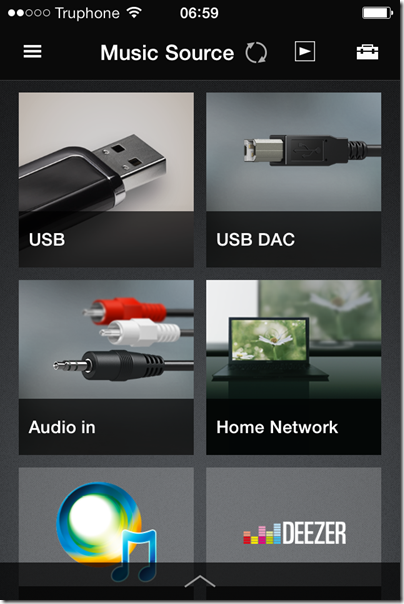
The remote has functions for power, input selection (Network, Bluetooth, USB-A, USB-B or analogue audio in), volume, mute, play/pause and skip.
This unit is flexible to the point of confusion. Here are the ways you can play back music:
- Apple AirPlay: play from iTunes over an wired or wireless network using Apple’s proprietary protocol.
- Bluetooth from Bluetooth-enabled devices such as smartphones or tablets. Uses A2DP (Advanced Audio Distribution Protocol) for best quality.
- From a DLNA-compliant music server on your network. Sony’s free Media Go will do, but there are quite a few of these around.
- Audio in using an old-fashioned 3.5mm jack cable.
- Direct attached USB storage. I had limited success with this, but did manage to play some FLAC files from a USB stick. It is designed for just a few files.
- Direct USB connection to a PC or Mac. In this mode the unit is a USB DAC. This is how you get the very best quality.
Supported formats are MP3, AAC, WMA, WAV, FLAC, and DSD via USB after firmware update. ALAC (Apple lossless) is not listed, but an Apple lossless file I created played fine from a USB stick, from which I conclude that it supports that too.
So how is the out of box experience? The first thing you notice is that this thing is heavy – 4.6kg. Despite its relatively small size (about 430 x 133 x 125mm) it is not all that portable; I mean, you can move it about if you like, but as well as the weight there is no handle and it should be moved with care; it is also mains-only.
The introductory manual gives you several ways to get started. It covers only wi-fi connection; if you want to use a wired network, Bluetooth or USB connection, you are referred to the online manual here. Otherwise, you are offered instructions for iOS, Android, PC or Mac. I have a Sony Xperia (Android) smartphone so I took that option; possibly a mistake.
I tried to follow the setup guide. I have a Sony Xperia (Android) smartphone. I downloaded the recommended SongPal app and successfully paired the phone with the speaker with NFC (tap to connect). The app prompted me to enter my home wifi password, but I was not successful; it just did not want to connect and kept on prompting me. I got hold of an iPhone, tried SongPal on that and was able to connect. Odd.
Once up and running it was time to play some music. I was able to play direct from the phone (Bluetooth streaming) without any problem. My results with DLNA were mixed. I have Logitech Media Server on the network which supports DLNA. Bizarrely, this usually shows up as a source when using the Android SongPal, but not when using the iOS SongPal. It worked at first, but then I started getting “Playback failed”. I had better luck with Windows Media Player over DLNA, and also Sony’s own Media Go.
That said, even when it is working I don’t much like the DLNA option. There is no search option and if you have a lot of music you do endless scrolling. This seems to be a feature of DLNA rather than the fault of SongPal, and a reason why it will never catch up with iTunes/AirPlay or Sonos.
SongPal also supports various apps such as Tunein (internet radio), Music Unlimited and Deezer. You can also add apps such as Google Play. This is a tad confusing though. Tunein seems to be built-in; you can select a radio station, play, turn off your smartphone and it keeps going. Choose Google Play though and it plays over Bluetooth from your phone; disconnect the phone and the music stops.
Since Tunein appears to be baked it, it is a shame that you cannot use the radio from the remote without needing SongPal.
If SongPal is not working for you, or if you have a non-supported phone such as Windows Phone, you can connect over the network. The manual suggests that you do a direct connection to a PC using an Ethernet cable, in which case the unit will likely show up in a web browser on 169.254.1.1. However if you connect the Ethernet cable to a switch (such as a socket on the back of your broadband router) it will show up on whatever IP number is allocated by the router; you can find it by looking at DHCP allocations, a bit tricky. There is also a WPS button for instant connection if your wireless router supports it (mine is disabled for security reasons).
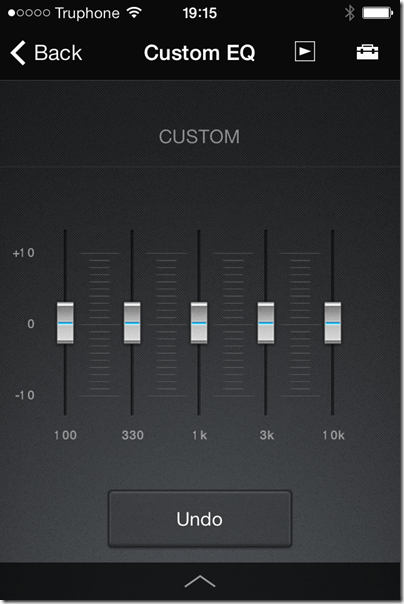
Wireless configuration through a web browser, once you get there, is really easy. You can even set a fixed IP address if you want. However, the browser configuration does NOT give access to all the features of the unit; it is mainly for network configuration. The SongPal app has additional settings, including EQ, a setting called ClearAudio+ which does who knows what, and DSEE HX which is meant to enhance lossy audio files such as MP3. That’s unfortunate; not everyone uses iOS or Android. That said, SongPal is not much fun to use anyway so you are not missing too much.
Once the unit was up and running I tried a few other modes. I ran up Apple iTunes and tried AirPlay, which works great, though with the usual AirPlay annoyance of a pause when connecting. When using AirPlay, you can use the pause, next and back buttons on the supplied remote. These don’t work in all modes, another point of confusion.
What about playing high resolution music or DSD? I was excited about this possibility so keen to get it working. I even have some DSD downloads to try. Discovering how was a bit of an adventure. You need to do two things.
First, update the firmware, by connecting over wifi and using the otherwise undocumented update button on top of the unit (check Sony’s site for full instructions). You need at least firmware 2.05.2.01.
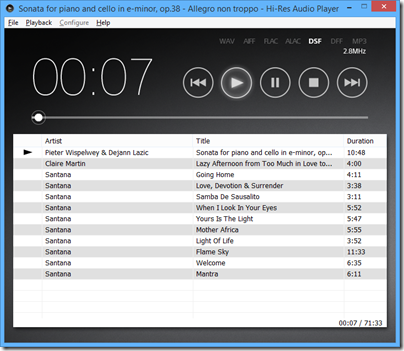
Second, find and install the Hi-Res Audio Player for PC or Mac on Sony’s site. Third, get a USB cable (not supplied) and connect it to a PC.
The downloads to get this working are here.
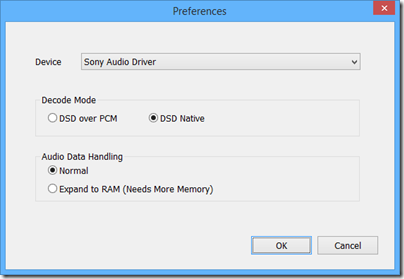
I was rewarded with excellent sound quality, though the audio player software is basic. On my DSD downloads I could see, for example, 2.8MHzs DSF indicated, and the configuration offered “DSD Native”, so I believe this thing really is a DSD DAC (though who knows, it may convert to PCM internally).
Once connected in this way, you can also set it as the output for other audio software such as Foobar 2000 or iTunes.
The sound
What of the sound though? The SRS-X9 has seven speakers: 1 sub-woofer, two midrange, two tweeters and two super-tweeters. This means you get mono for the lowest frequencies, but that it not really a disadvantage as low frequencies are not directional and you don’t get much stereo image with this box anyway.
In addition, there are two passive bass radiators.
As you would expect from a unit at this price (nearly £600 in the UK) and with some audiophile pretensions, the sound is very good. In its class – as a single box wireless speaker – it may be the best I’ve heard. It easily beat a Squeezebox Boom, sounding both bigger and cleaner. I also thought it had the edge over an Audyssey Lower East Side Audio Dock Air, which is another AirPlay speaker with good sound, though the Audyssey offers deeper bass.
The SRS-X9 does go relatively deep though, and the bass is clean whereas the Audyssey tends to boom a little.
The sound is not faultless though. It is a touch bright and can get a little strident at higher volumes. Vocals can have slightly exaggerated sibilance. Stereo imaging, as mentioned above, is poor, thanks to the close proximity of left and right speakers. The sound is exceptionally clean, which is hardly a fault, but worth noting if you like to get down and boogie; you might find the SRS-09 overly clinical.
These are reasons why the SRS-09 will not replace a traditional home stereo for me. I also like having separate speakers either side of my PC screen, so this is not perfect for that role.
HOWEVER as a minimalist and good-looking single box speaker this is excellent; perfect for a sitting room if you do not want the clutter of a traditional home stereo, or for somewhere else round the house where you want high quality music.
The sound over USB is best, and ideally I would suggest parking a Mac Mini or similar small computer next to it and using it that way. On the other hand, AirPlay also works well and in conjunction with Apple’s Remote app this is a convenient solution. Bluetooth can be handy too.
A few other notes. Sony has gone for an understated design, and the buttons on top of the unit are completely flat and in fact mostly invisible unless you hover your hand close by – it uses a proximity sensor. Clever, but easy to hit a button by accident if you are repositioning the device.
The appearance is glossy black, looks nice but gets dusty easily. Sony supplies a little black cloth for polishing. Unfortunately the super tweeters on top are surrounded with a slightly sticky area which attracts dust and is hard to clean; this might bother you if you are meticulous about such things.
The front grille can be removed with two supplied magnetic tools; Sony says this give a “more dynamic sound” though the difference is not great.
It is a shame that there is no audio output port, neither for headphones, nor for external speakers. You cannot use this as a DAC for another stereo system, for example.
An S/PDIF optical digital input would also be handy, as this is more universally compatible than USB for wired digital input.
Other weak points are the fiddly setup, reliance on a mobile app for some settings, general unreliability of DLNA, and some problems which mysteriously disappear when you turn off and on again (with so many input options it is not surprising that the Sony gets confused sometimes).
Conclusion? There is a ton of technology packed into this box and it does sound good. I like the option to play back native DSD even though it is all a bit mad; it is doubtful that the inaudible higher frequencies really make any difference, and there are compromises elsewhere such as the mono sub-woofer and limited stereo image that more than outweigh any benefit from high-resolution (a controversial subject). Never mind though; Sony has taken trouble over the sound and it shows.
Good points
- Flexible streaming options
- High quality sound, exceptionally clean
- Compact, minimalist design
- Smooth AirPlay support
- Support for hi-res PCM and DSD audio files when connected via USB
Bad points
- Dependence on iOS or Android apps for some features, no support for Windows Phone
- No headphone socket
- No audio output for connection to other hi-fi kit
- No S/PDIF optical digital input
- Limited stereo image and sound too bright on some material
Specifications
- Size: 430x133x125mm
- Weight: 4.6Kg
- Power consumption: 50w
- Power output: unknown though Amazon quotes “154w”
- Frequency response: Sony quotes “45Hz to 40kHz”.
- Drive units: 1 sub-woofer, 2 passive bass radiators, 2 midrange units, 2 tweeters, 2 super-tweeters
- Streaming support: Bluetooth audio, AirPlay, DLNA