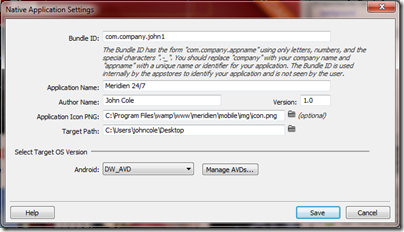
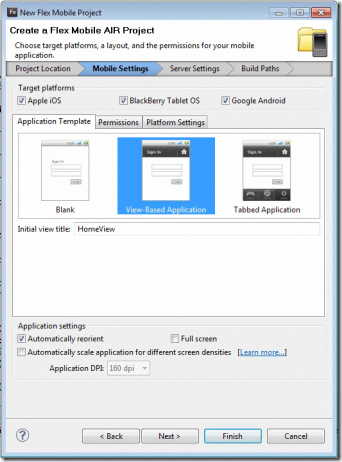
I have been trying several cross-platform development tools for mobile, and today I set out to create an Adobe AIR app for Android using the new Flash Builder 4.5, available separately or as part of the Creative Suite CS5.5.
I made another calculator app, which may seem boring but gives me a chance to compare like with like.
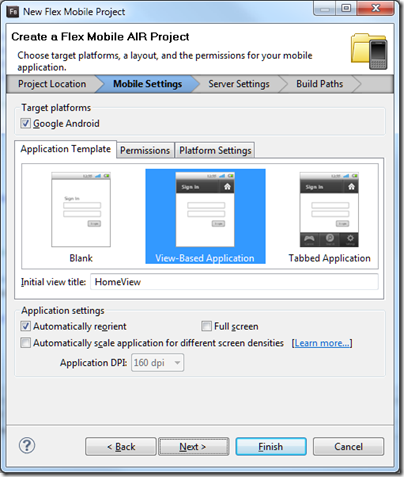
You get started by running up Flash Builder and creating a new Flex Mobile Project.
The disappointment here is that only Android is supported, so it is not all that cross-platform. According to Adobe’s Andrew Shorten:
An update to Flash Builder, scheduled for June 2011, will provide additional options to package Flex applications for Apple iOS and will include built-in support for packaging both Flex and ActionScript applications for BlackBerry Tablet OS.
so we have not got long to wait.
Flash Builder is based on Eclipse. The IDE is slow at times, for example when switching to visual design mode, but the platform is familiar to many developers and it feels reassuringly enterprise-ready. I find it a productive environment.
I laid out a screen with buttons and a label to display the output. The alignment tools work well although I made them a little too small as you will see shortly. Then I started writing code. The language of Flash Builder is ActionScript, which is based on JavaScript.
Here I met my first little annoyance. You can easily create a click handler for a button by right-clicking in the designer and choosing Generate Click Handler, or by clicking Generate Event Handler in the properties window. However, I thought it would be smart for most of my buttons to share the same event handler. All I need to do is to read the label of the button which was clicked, and pass it to my addnum routine that processes the input:
protected function btn_clickHandler(event:MouseEvent):void
{
var theButton:Button = Button(event.currentTarget);
addnum(theButton.label);
}
This works fine, but the IDE does not let you select an existing event handler for a button. You can paste it in, or add in in the source code editor, which is what I ended up doing. The source code editor is rather good, with excellent code completion, hover-over help for keywords, and so on.
The second annoyance was with the label. I wanted to add a border. I selected the label but could not see a border property. I went to the full list of properties and found exotic things like dominantBaseline in the style list but still no border.
Then I found this in the reference for a label:
Borders are not supported. If you need a border, or a more complicated background, use a separate graphic element, such as a Rect, behind the Label.
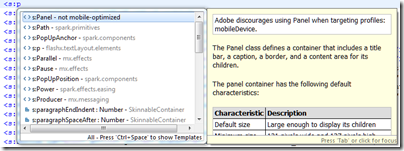
I wondered if a panel would work, and started to type it in the editor:
Well, it looks as if Panel is overkill for simply getting a border, but it was interesting to see the editor report that “Adobe discourages using Panel when targeting profiles: mobileDevice”. I decided to do without a border for the moment.
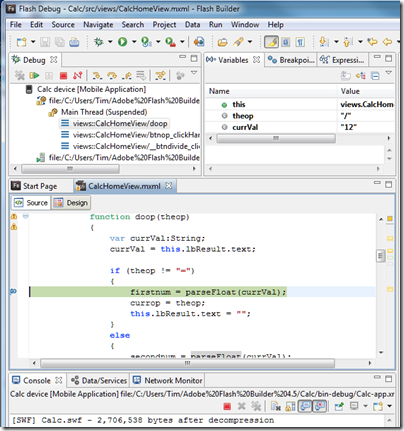
I finished the coding and successfully ran the project in the Android simulator. Next, I attached a device and created a new Run Configuration for a device attached via USB. I plugged in my HTC Desire running Android 2.2. Provided USB debugging is enabled on the device, this works well. Not only could I run on the device; I could also set a breakpoint and debug on the device. Everything was a bit slow in debug mode but it worked.
Finally, I built a release version using Export Release Build on the Project menu. You have to sign the package, but there is a wizard to create a certificate for testing.
Here it is on the device – as I mentioned, the size of the buttons needs a little work:
So how is performance, bearing in mind that the app is trivial. Well, the good news is that performance is OK, though launch is a little slow, except for one thing that I have not figured out. Sometimes I touch a button, and see the graphic effect as the button depresses, but the input does not register. It seems most prone to this just after launching, and usually a second tap works fine.
The vsize reported for the app process by the Dalvik Debug Monitor is around 200K, similar to that for the PhoneGap version.
Overall I am impressed, though I would like to understand the button issue, and I am beginning to wonder if my year-old HTC Desire is a bit under-powered for AIR. Device performance is improving rapidly, and Flash optimization is part of the design process for mobile graphics chips, so my guess is that AIR will be more than viable as a cross-platform toolkit for mobile. You also get the benefit of all those lovely Adobe design tools.