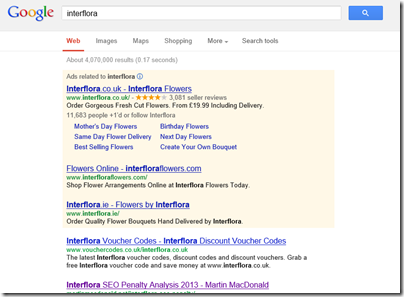
Via Martin Belam’s blog I came across this account of how the well-known flower vendor Interflora has, it is claimed, been penalised by Google for violation of its webmaster guidelines on paid links:
Searching for the terms [Flowers], [florist], [flower delivery], [flowers online] and hundreds of other related search terms yielded the interflora.co.uk domain in first place – until yesterday afternoon. Now the website does not even appear for its own brand name.
Possibly by no coincidence, an official Google post reminds us of the rules:
We do take this issue very seriously, so we recommend you avoid selling (and buying) links that pass PageRank in order to prevent loss of trust, lower PageRank in the Google Toolbar, lower rankings, or in an extreme case, removal from Google’s search results.
I find this troubling. Here are a few statements (some may be contentious) that taken together will, I hope, express why.
1. Google has a market-dominating position in search, certainly in the UK. With good reason, users wishing to visit Interflora’s site are more likely to type “interflora” into a search engine, probably Google, then to type the URL directly. The combined address bar and search box in most browsers encourages this. Many users probably do not appreciate the difference. Of course they might also type “order flowers” into the box, delegating to Google the responsibility for finding suitable sites.
2. In consequence of 1, Google has direct and immediate power over the amount of business that will be achieved by a company trading online. In some cases that might be make-or-break, in some cases not, but it is a significant influence.
3. A further consequence is that Google’s search and ranking algorithms form an incentive to businesses to do all they can to climb higher in the search ranking. Since this appears to be influenced by incoming links (though probably less so than it once was) Google’s algorithms attempt to judge which incoming links are meaningful and which are not. Paid links fall into into the latter category, hence the guidelines which prohibit them.
4. Despite (3) above, the internet is infested with paid links and link exchanges. Even running a small site like mine, I get thousands of paid link and link exchange requests every year. The implication is that Google is not all that good at ignoring and/or penalising them, otherwise the activity would cease.
5. Worth noting: web site owners are free to accept paid links and vendors are free to buy them. They are not doing wrong. The only disincentives are first, whether you want to fill your site with worthless links, and second, whether you will be penalised by Google for doing so.
6. Google’s process for determining whether or not a particular web destination is down-ranked is not transparent. This is for good reasons, insofar as a transparent process would arguably be easier to game. On the other hand, this also means that a business which is penalised has no recourse other than to plead with Google, unless it felt inclined to experiment with legal action (prohibitively expensive and uncertain for most).
7. In fact there is another option, which is to advertise with Google, a form of paid link which the search giant is happy to accept. It seems to me obvious that this form of advertising is designed to look similar to unpaid search results, despite some small effort to distinguish them with small print and a light background colour change:
It is not clear to me that this intermingling of paid and organic results is in the user’s best interests.
8. It is also obvious that advertising in this form is more important in cases where a business is absent from organic search results. It follows that Google has a direct incentive to penalise businesses by downranking them, since it has the potential to bring more advertising business. Please do not misunderstand: I am not accusing Google of doing this and have no reason to believe that it does.
9. Users of Google will be grateful that it attempts to improve the value of its search results by reducing the influence of meaningless incoming links. On the other hand, I find it difficult to understand why a user who typed “interflora” into Google would not want to see the official site at the top of the list, since it is a legitimate business and not in any sense malicious. Of course they do in fact see this, judging from my own experiment minutes ago, but it is an advertisement and not an organic link. The top organic link is not Interflora’s own site.
10. Pause for thought: what would be the effect on Google’s business if it put ads below organic search results rather than above?
11. The only rationale for (9) above is that Google considers it worth inconveniencing its users (presuming you do not accept that it simply wants to sell more ads) for the sake of the higher objective of penalising sites which, in its view, breach its guidelines.
12. We all have a choice whether to use Google or not; but this choice is not one that fixes the problem. The problem, rather, is the choice which our customers or potential customers make, over which we have no control.
13. It is a company’s duty to maximize returns to its shareholders. Making a profit is not wrong, and Google is entitled to design its search algorithms and web site as it wishes. None of the above is intended to imply that Google is doing wrong.
14. Despite (13) above, the combination of this concentration of power in a single business entity, the lack of transparency in its procedures, and the difficulty smaller businesses (in other words, almost everyone else) have in fixing issues, is something I find troubling.
15. It is also worth noting that the power of a dominant search engine goes beyond SEO (Search Engine Optimization). There is a long-standing debate over how easy it should be to find sites which offer illegal music downloads, for example. Another recent case I encountered showed how Google can make it hard to find a business in the real as well as the online world. I also note the influence of search engines on education, as the first destination of students and pupils looking for answers, and on human knowledge in general.
These issues are both complex and important. Should Google be regulated? Should all search engines be regulated? I do not know the answer, but believe that the question merits wider discussion. In this instance, it is not obvious to me that the free unregulated market will achieve the best outcome.